Evolution
Evolution is among the most substantiated concepts in science and is the unifying theory of biological science. Charles Darwin co-originated, with Alfred Russel Wallace, the theory of evolution by natural selection. His masterwork, the 1859 "Origin of Species," offered ample evidence for evolution having occurred, as well as the first strong explanation for its mechanism, natural selection. Modern evolutionary theory incorporates these concepts: species change over time; genetic mutations are responsible for the changes; individuals with beneficial genetic mutations will survive preferentially compared with their competitors, in a process known as natural selection; those successful individuals' more numerous offspring will spread the beneficial genetic constructs throughout the population; when enough genetic changes reproductively isolate a population, that population has become a new species. Here you'll find news and information on evolution and the battle with proponents of so-called creation science.
Latest about Evolution

Which animals are evolving fastest?
By Marlowe Starling published
The "fastest evolving vertebrate" title is hotly contested, but here are a few contenders.
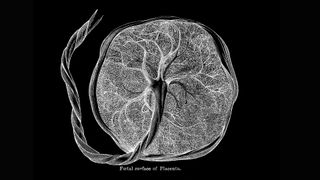
'I have never written of a stranger organ': The rise of the placenta and how it helped make us human
By Jules Howard published
"Human evolution has occurred both due to, and in spite of, the placenta. Every pregnancy, unthinkingly, must navigate a careful path through it. Every menstruation is testament to it. It is partly why menopause exists, to give individuals an escape from the energetic costs associated with its imposition."

Ancient relative of 'living fossil' fish reveals that geological activity supercharges evolution
By Stephanie Pappas published
The ancient coelacanth, which has existed for some 419 million years, never stopped evolving despite its reputation as a "living fossil." A new discovery reveals that it evolved faster when plate tectonics were most active.

How fast does evolution happen?
By Marlowe Starling published
Measuring the pace of evolution is tricky, but some species can evolve as quickly as a few generations.

Defense system common to all life came from 'Asgard'
By Tia Ghose published
Defense systems found in all complex life, including the human body, came from primeval microbes known as 'Asgards.'

Evolution: Facts about the processes that shape the diversity of life on Earth
By Tiffany Taylor published
Discover interesting facts about how evolution works, the different patterns that can emerge from evolution, how quickly organisms can evolve, and whether evolution is a random or ordered process
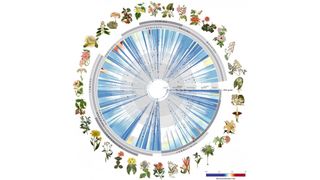
What is the 'tree of life'?
By Emma Bryce published
The tree of life maps out the relationships between all living things, and it's in constant flux.

Continental collision 2.1 billion years ago may have sparked '1st attempt' at complex life on Earth
By Patrick Pester published
Researchers have laid out the case for complex life evolving 2.1 billion years ago, but not everyone is convinced it started so early.
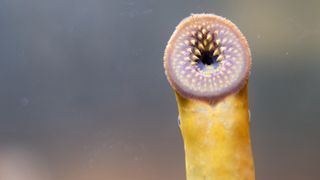
Human origins tied to ancient jawless blood-sucking fish
By Patrick Pester published
Researchers have traced cell origins critical to vertebrate evolution by studying a group of primitive, bloodsucking fish called lampreys.

Last Chance Lake: The unusual 'soda lake' with conditions that may have given rise to life on Earth
By Sascha Pare published
Scientists consider Last Chance Lake to be an analog for lakes that may have existed on Earth 4 billion years ago and contained the ingredients for early life on our planet.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.
